Certain learners exist who possess what seems like complete immunity to whatever pedagogy they’re subjected to. College students are a good example. Professors rarely have pedagogical training, which is perhaps the most ironic thing about those in charge of training pre-service primary and secondary teachers, but most college students are able to persist through a lack of solid pedagogy. How? Using their interests, some independent learning skills, and a bit of determination. Polyglots are another good example. They’ll learn many languages under all sorts of conditions that don’t transfer to others, claiming they found “the secret,” yet relatively few who adopt their “methods” report success (except for other…polyglots!). Upon thinking this over, many high school students—and not just those studying a second language—are often pedagogically immune, too. These students manage to pass courses even when teachers have wacky pedagogy with unhelpful practices. Consider the teacher using some pre-fab curriculum with loads of busywork. Students will put up with all that busywork. They might not learn much, but they’ll earn credit, then graduate. In that sense, then, these students made it through. They were immune (though not to learning…which we’ll get to). They just made it past the next level. They…”succeeded.”
Continue reading4%er
100% Coverage ≠ 100% Comprehension
A question by a member of the Latin Best Practices FB group prompted me to look into text coverage, which ultimately led me to comprehension. These are two ideas that a lot of people have misinterpreted, much like the “4%er” figure, and even “90% target language use.” I’m thinking people have a hard time with mathematical concepts, and maybe we should avoid percentages moving forward. But first, we should take care of what damage has already been done by looking at simple examples right away:
Text Coverage
Text coverage is measured by tokens. There are five tokens in the sentence “the bird sees the cat.” Two of the tokens in that sentence happen to be the same word. Therefore, “the” represents 40% text coverage. If the reader doesn’t know “the,” they have a text coverage of 60%. The reader who knows everything except “cat” would have a text coverage of 80%.
Comprehension
Comprehension is a different idea entirely. If the reader who doesn’t know “cat” were asked “what does the bird see?” and it were scored, they’d have a comprehension score of zero. If they were asked two questions about the bird, and two questions about the cat, their score would be 50% comprehension with their 80% coverage of the text. Not the same thing.
Reading
Laufer et al.’s research shows that learners need a text coverage—not comprehension—of 98% ideally to read with ease (and 99-100% whenever possible), but that’s just getting through the reading. That 98% figure is just the start of comprehension.
Hold up.
Yeah, that’s right. Knowing 98% of a text—STOP!!—Remember the first section on tokens. It’s not 98 out of 100 different words, but 98 of 100 tokens (i.e. some words probably repeat). So, knowing 98% of a text doesn’t even guarantee comprehension of what is read. That’s quite the trip, isn’t it? It gets worse when we look at some findings from one of Eric Herman’s Acquisition Classroom Memos on exactly how [in]comprehensible reading can get with what seems like decent text coverage.
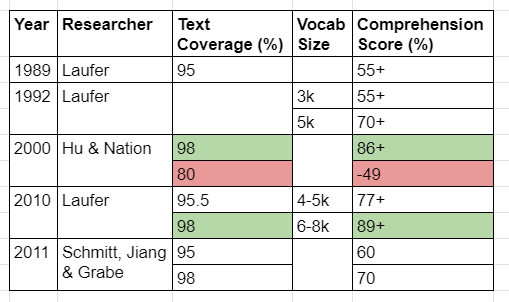
There’s a lot in that chart, but compare the text coverage to comprehension scores. Even 95% text coverage can get woefully low comprehension (55%). Keep in mind that the higher scores are still in the “most” range, as in learners are understanding most of what they read when they know 95%+ of a text. Also, those vocabulary sizes are incredibly high for what the majority of K-12 teachers should expect from their students. Eric also adds some context to the research:
“For the most part, the above reading studies were done with high proficiency students, ungraded and academic texts, and count word families. A reasonable prediction is that even higher text coverage and vocabulary size numbers are required to enable adequate comprehension of graded texts by lower level proficiency students. And this is not considering levels necessary for a confident and pleasurable reading experience, which would undoubtedly be even higher!“
Higher would be 100%. Let’s make sure we set the record straight:
- Students need to know 98% of a text to read it with ease.
- Reading with ease from knowing 98% of a text can still result in much lower comprehension scores, like 70%.
- Coverage ≠ comprehension
Providing students with texts of 98%…even 100% coverage of known words is step zero. It’s actually the minimum hope we could have for students reading with ease with high levels of comprehension. It turns out that text coverage isn’t very important to look at, because even knowing 100% of the words doesn’t guarantee 100% comprehension. It all goes back to vocab as top priority, sheltering whenever possible so gradual exposure to new words increases vocabulary without the burden of incomprehension. What does this mean for class? Probably using even fewer words than you think! Students can’t magically learn thousands of words, so if we expect them to comprehend high levels of what they read—especially during any kind of independent reading—we must use and create texts with a very limited number of words.
1969: 50 Years of “4%ers”
Just a few months after the moon landing, Superintendent John Lawson (Shaker Heights, OH) gave a speech at the Symposium on Foreign Language Teaching at Indiana University. Its age certainly shows. Then again, were it not for the typeface, you’d think some of these statements appeared yesterday in a blog! I find it striking that such “progressive” and “controversial” ideas have been discussed for 50 years, pretty much coinciding with the civil rights movement, yet without much fundamental change to either. There’s no excuse for the latter. As for second language teaching, that’s slightly more understandable considering the field of Second Language Acquisition (SLA) was hardly established by the late 60s.
To give you a sense of how relevant Lawson’s ideas are today, look at this statement addressing the importance of compelling topics, and what now has become criticism against using unadapted texts driving the AP Latin problem:

There’s also a section, while brief, managing to address topics like teaching to the test, teacher perception of status in their field, elitism, exclusivity, ineffective pedagogy, compellingness, connectedness, comprehensibility, and confidence. All that back in 1969. Holy moly, right?!

That speech also happens to be the source of the “4%er” term that Keith Toda just shared in his latest (and last-for-a-while) blog post. Now, Keith is somewhat of a self-proclaimed man of the shadows not really active on social media, so my first thought was that he didn’t know the “4%er” term doesn’t really come up these days. In fact, I had to go back to a 2015 moreTPRS list email to search for the references contained in here! But maybe that term is exactly what teachers need to be reminded of right now. Let’s start with its history:
Continue reading