I haven’t given midterms in years. Back when I did, though, it was a self-assessed analysis of fluency writes (I no longer do any sort of timed write, either, but that’s another story). Now, aside from the infuriating last-minute “all courses must have a midterm” decision we got hit with coming back from holiday break, I had a major discovery when giving the [ungraded] midterm this year.
Continue readingStrategies & Activities
Translating Isn’t The Problem
When the updated Standards for Classical Languages were shared, one key difference was the near-omission of the word “translating” as an active task, mentioned just once under a description of advanced learners at the postsecondary level (i.e, “Learners conduct research in the target language or assist in the translation of resources for the benefit of others.”), and then appeared in one example learning scenario submitted by a university professor. Granted, these standards have been in draft form—somehow—since 2017, but Latin teachers have been lauding that lack of “translation,” preferring nowadays that students focus more on reading Latin than doing translation exercises. However, it turns out that translating, per se, isn’t the problem…
Continue readingFlex Time & Google Days
“You teach the kids you have.” I like this nugget of wisdom. It doesn’t matter if previous classes of students did this or that. Everyone must teach the students they have in the room, not anticipated students, or former students. Sometimes what the students in the room don’t know can be surprising, but the only thing that matters is what we do about it. For example, I’ve been perplexed by the lack of digital literacy I’ve been seeing with incoming 9th grade students. Rather than shake my head, pretending that lack of skill isn’t my problem, I’m going to do something about it. I’m going to do something even if it has less to nothing to do with Latin. Why? Because I teach the kids I have, and these kids need to be able to navigate Google Classroom, and I’m tired of pretending it’s fine. The plan? Each week, students will have 20 minutes to organize their learning after another 20 minute independent learning session. The latter part isn’t really new, so let’s start with that:
Flex Time
This independent learning time worked out really well last year. I checked my planning doc and saw that between December and June we had Flex Time a total of eight times. I’ve curated the options, most recently removing Quizlet since I find it less useful when not immediately followed by a whole-class Live session before reading the text. New for this year will be to encourage an ongoing project. Is the goal to read as many novellas as possible? Is the goal to work through an entire textbook? Is the goal to learn about a specific Latin-related topic? Instead of bouncing around the Flex Time options every few weeks or so, students will now choose an ongoing option for this new weekly routine every Wed/Thurs. Yes, they can switch if they really want to, just as long as they reflect why (e.g., “I liked the idea of having textbook structure, but I think Caecilius is boring.”).
Google Days
The second half of Wed/Thurs each week gives students time to check feedback and submit learning evidence (Google Classroom) for Latin class. Once done, or if already caught up, the remaining time is for checking school email (Gmail) and responding to other needs, such as correspondence with teachers, and/or completing other class Google Classroom assignments. No, it does not bother me if a student ends up doing 8 minutes of math at the end of Latin. I’m teaching the students I have, and it’s clear that they need something like this. What I will do is make sure this rolls out smoothly. What I won’t do is hang out at my desk and overestimate my student’s independent learning capability. This kind of work with 9th grade requires heavy monitoring, not unlike the first minutes of independent reading. That is, if I think students are going to magically grab a book and be quiet on their own within 10 seconds, I’m fooling myself. Yet every time I take those first moments to ensure the majority of students—yes, majority, because we can’t have it all, all the time, everywhere, all at once—settle into a task, I’m always rewarded with my own quiet time to read, with the occasional look up, make eye contact, and stare down the kid who’s goofing off until they get back to the book. It works. You just have to commit to both: monitor the room, getting kids on task at the start of an activity, and being unwavering with a teacher look at the ready.
So, the second 20 minutes of Wed/Thurs is also for students to add learning evidence, submitting work from the previous week in addition to what they did during Flex Time. For example, they could attach a notebook pic from Mon/Tues annotation task, as well as a statement about something they learned from their Flex Time findings, how much they read of a book, what they were working on, etc.
Pedagogical Immunity
Certain learners exist who possess what seems like complete immunity to whatever pedagogy they’re subjected to. College students are a good example. Professors rarely have pedagogical training, which is perhaps the most ironic thing about those in charge of training pre-service primary and secondary teachers, but most college students are able to persist through a lack of solid pedagogy. How? Using their interests, some independent learning skills, and a bit of determination. Polyglots are another good example. They’ll learn many languages under all sorts of conditions that don’t transfer to others, claiming they found “the secret,” yet relatively few who adopt their “methods” report success (except for other…polyglots!). Upon thinking this over, many high school students—and not just those studying a second language—are often pedagogically immune, too. These students manage to pass courses even when teachers have wacky pedagogy with unhelpful practices. Consider the teacher using some pre-fab curriculum with loads of busywork. Students will put up with all that busywork. They might not learn much, but they’ll earn credit, then graduate. In that sense, then, these students made it through. They were immune (though not to learning…which we’ll get to). They just made it past the next level. They…”succeeded.”
Continue readingIndependent Reading Lessons
When it comes to the fairly recent phenomenon of independent choice reading for Latin, how do students choose what to read, and what do they do when flipping through the book? These simple lessons get students thinking about why we want them reading level-appropriate books and to understand how important it is to choose ones that feel easy, as well as what we mean by actual reading (vs. some other close reading, skimming, etc.). Most importantly, perhaps, we want to show students the difference between what a translating experience and a reading one is. These two lessons are scalable, but I recommend taking at least 15 minutes.
A) How To Choose A Book (requires novellas with full glossaries)
- Students choose 3 random books from the library.
- Read/”read” that book, using the glossary for unknown words (~3 minutes).
- Count up total words read/”read.”
- Repeat with other two books.
- Share & Discuss.
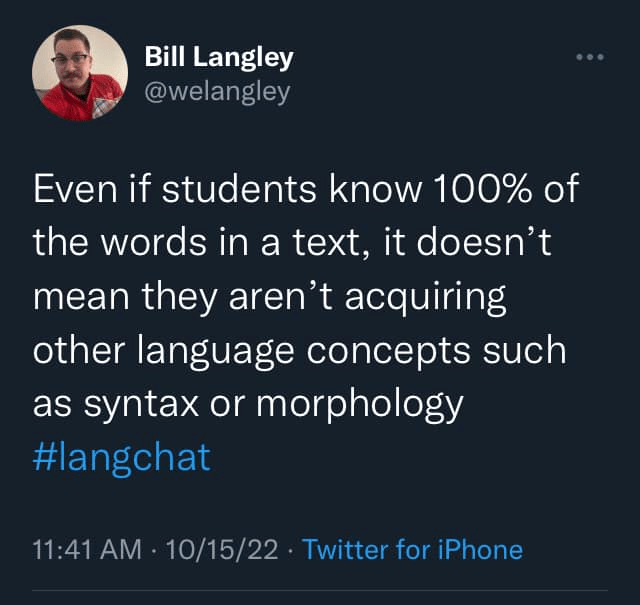
Students should have a range of words read (e.g., 20 to 200). Mention that some might have been unlucky enough to have chosen the three highest level books. Obviously, they’re not gonna get as much out of a higher level book. The main thing to point out is that the book each student read the most of should be the kind of one they choose during independent reading. Strategies like “if you have to keep flipping,” or “if it feels too much like work” should send the message to get a book that’s at- or below-level, resulting in optimized input. N.B. get this poster from Eric Herman if you don’t already have it. I constantly point to it during class to show priorities (i.e., 1 = lots of Latin, 2 = must be comprehensible…). Once they get the idea of which kind of reading level will be most helpful, because you still get a lot out of books that are easily read and below-level (see Bill’s tweet below), do another mini lesson on how to read.
B) How To Read (or, Reading vs. Translating)
- Read book as fast as possible, skimming and getting the gist of what’s going on (~1 minute).
- Count up total words read.
- Go back and read for understanding, as if they had to tell someone who didn’t know Latin a) what the story is about, and b) what’s happening right now in the chapter (~1 minute).
- Go back and read as if to memorize and describe everything with incredible detail! (~1 minute).
- Share & Discuss.
The main point to make is that #1 is waaaay too fast. All that input doesn’t matter if students can’t recall what happened, or have no idea what’s going on. #3 is waaaaay too slow. They’ll never get enough input reading with that much attention to detail while trying to memorize. #2 is what we’re going for: reading with enough comprehension to retell the story to someone else.
Talk, Read & Reread
I’ve been using the basic Talk & Read class structure for a while (i.e., a greeting, quick discussion, and/or some activity “by ear” for about 5 to 20 minutes, then reading, reading, reading for the remainder). That was when I had 40 to 60 minute classes for years. However, switching to an 85-minute block schedule last year really fucked things up. Now, classes feel way too long, I’m exhausted, there’s too much time between class days (i.e., 48 hours) so “the din” of Latin in students’ minds grows dim, and absent kids miss out big time (i.e., now 96-120 hours from class to class if absent just one day).
It turns out that I didn’t write much about the block schedule messing with things last year aside from a blog post or two. Granted, 2021-22 was the first year back from remote learning. That came with unique challenges, and the schedule change didn’t help. Btw, this is my 10th year teaching and my 10th schedule. Even when I stayed at the same school for more than a year, the schedule changed each one. I’m now in the 6th year at the same school. 6 schedules. Anyone wanna place a bet as for next year will hold? So, 2021-22 was a big calibration year for all sorts of reasons, and it’s taken me until right now to actually identify how much the schedule has negatively impacted first year language students. But I have a solution…
Continue readingDraw & Discuss [Collaborative] Storytelling
Last year, I observed Emma Vanderpool’s class for about 20 minutes of storytelling. What I saw was a combination of storytelling while drawing (e.g., Storylistening), and Write & Discuss/Type ‘n Talk. Emma told the story of Romulus & Remus as students listened as they copied her drawings and any Latin she wrote on the board to accompany the story. She asked questions between all the statements and drawing, and established meaning of new words right on the board. The result was a smash doodle kind of collage. The experience was input-rich and highly comprehensible. Students were actively listening, drawing, responding, and asking for clarification.
Last week, I observed my student teacher run the same activity for Latin 1 students with a version of Berg’s ursa story from this month’s Writing Challenge #2. The experience was a hit, and just as effective. It was almost pacifying, too, like a waaaaaaaaay more interesting dictatio, and I plan to do this a lot more throughout the year. I also got thinking how this could easily be turned into collaborative storytelling, giving each student something to do while the story unfolds: draw! Perhaps part the story is established, and I do Draw & Discuss for half the time, then start storyasking details. I draw, they draw, etc.
Writing Challenge #3: Description
As we’re winding down the month’s writing challenges, let’s recognize that over just a couple weeks, contributors produced nearly 3,000 words of Latin for the beginner. These short stories share some themes and common vocab. Not bad at all! While sheltering vocab is not everything, it’s most things, but let’s add something onto keeping word count low, shall we? Descriptions. Among other uses of description, a character’s quality or how they do some action becomes an instant question for students: “are you also like the character?” or “would you do things the same way?”
So, Challenge #3 is to write a highly descriptive short story using as few of the following core verbs and function words as possible in order to focus on description:
- esse, habēre, velle, īre, placēre
- et, quoque, quia, sed
- ā/ab, ad, cum, ē/ex, in
- ergō, iam, nōn, subitō, valdē
For Challenge #3, there will be an overall unique word limit (excluding names, and different forms of words). Also, don’t forget about referring to the cognate list for adjectives, and don’t forget to make adverbs from them!
BOSS level sheltering: no more than 15 words
CONFIDENT level sheltering: no more than 25 words
NOOB level sheltering: no more than 35 words
Here’s the link for Challenge #3. And here’s where I’ll put the stories once they start rolling in.
Comprehension Establishers & Question Types/Possibilities
I end up learning at least one thing each year from my student teachers, whether it’s some insight while observing, some reflection when we’re planning, or some new activity or strategy they suggest. Here’s a revelation worth looking into…
When scripting out some questions back in October, one example I gave was asking “class, which word means ‘again?’ Is it aliquid or iterum?” After a few more like this, my student teacher said “oh, it’s kind of like a comprehension check acting as a comprehension…establisher.” I paused for a moment, then realized yes, that’s exactly what that is. She put a name to what I’ve been doing for years, going way back to the 2016 sneaky quizzes when I’d use the T/F statements to establish meaning of words.
Comprehension Establishers establish meaning in the form of a question.
The difference in purpose between comprehension checks and establishers is subtle. Establishers aren’t intended to evaluate student understanding. They’re asked in a way that all but guarantees students make a form-meaning connection (e.g., “What word means ‘obscure,’ nocte or obscūra?”). A comprehension check, however, is often exactly that: to check whether a student understands, and if they don’t, then we establish meaning right away. In that sense, can an establisher bypass the check and then establishing meaning? Absolutely, but then there’s variety to consider. Might as well get some experience with both.
Question Types/Possibilities
Also discovered when scripting out some questions, it became clear to me that there are often too many possibilities. Instead of brainstorming every possible one, it’s probably more beneficial to settle on a couple question types and cycle through them while reading. For example, using one sentence, Mārcus ōrdinārius esse nōn vult, we could ask each of the following:
Contrary-To-Fact Personalized Q: vellēsne esse ōrdinārius?
Comprehension Establisher Q: Which word means “to be,” esse or vult?
Comprehension Checks: What does esse mean?
Content Q: What does Marcus not want?
But should we ask that many questions for one sentence? If so, should we ask all four questions for EVERY sentence in the chapter? I’m thinking “no,” and “no.” While on the one hand it would appear to provide the student with a great deal of support, on the other hand this process would drag out quite a bit. My recommendation would be to ask just ONE of those question types PER sentence and see how it feels. You might find that even one of those questions per sentence ends up being too many while reading. If so, scale it back to a question per section of two-three sentences, and then just cycle through the four question types. For example, if a short chapter has eight sections of sentences, you’ll ask a comprehension establisher q, a comprehension check, a contrary-to-fact personalized q, a content q, and then repeat. My advice is to identify the contrary-to-fact personalized q’s first, since it doesn’t always make sense to ask those. Then, fill in the rest. Print these out, and stick them in the book you’re reading. Remember, unused scripts already served a purpose: to get you thinking of how and what to ask students.
Writing Workshop & Challenge #2
People have all sorts of things to say about the Latin being written these days. Sure enough, the vocabulary decisions I made for writing Challenge #1 were questioned almost immediately. While there’s no need to defend any of those decisions, it’s definitely worth looking at why those “core” 19 words were chosen and how they’re useful for storytelling. So before we get to Challenge #2, consider this a mini little writing workshop. Cui dono…? No one in particular. Let’s take a look at those words…
Continue reading